Studies on Temporal Trends in Fish Community Structures in French Rivers
dat.maire2019.RdResults from studies examining changes in the abundance of fish species in French rivers.
dat.maire2019Format
The object is a list containing a data frame called dat that contains the following columns and distance matrix called dmat:
| site | character | study site |
| station | character | sampling station at site |
| site_station | character | site and station combined |
| s1 | numeric | Mann-Kendal trend statistic for relative abundance of non-local species |
| vars1 | numeric | corresponding sampling variance (corrected for temporal autocorrelation) |
| s2 | numeric | Mann-Kendal trend statistic for relative abundance of northern species |
| vars2 | numeric | corresponding sampling variance (corrected for temporal autocorrelation) |
| s3 | numeric | Mann-Kendal trend statistic for relative abundance of non-native species |
| vars3 | numeric | corresponding sampling variance (corrected for temporal autocorrelation) |
| const | numeric | constant value of 1 |
Details
The dataset includes the results from 35 sampling stations (at 11 sites along various French rivers) examining the abundance of various fish species over time (i.e., over 19-37 years, all until 2015). The temporal trend in these abundance data was quantified in terms of Mann-Kendal trend statistics, with positive values indicating monotonically increasing trends. The corresponding sampling variances were corrected for the temporal autocorrelation in the data (Hamed & Rao, 1998).
The distance matrix dmat indicates the distance of the sampling stations (1-423 river-km). For stations not connected through the river network, a high distance value of 10,000 river-km was set (effectively forcing the spatial correlation to be 0 for such stations).
The dataset can be used to illustrate a meta-analysis allowing for spatial correlation in the outcomes.
Source
Maire, A., Thierry, E., Viechtbauer, W., & Daufresne, M. (2019). Poleward shift in large-river fish communities detected with a novel meta-analysis framework. Freshwater Biology, 64(6), 1143–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13291
References
Hamed, K. H., & Rao, A. R. (1998). A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. Journal of Hydrology, 204(1-4), 182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00125-X
Concepts
ecology, climate change, spatial correlation
Examples
### copy data into 'dat' and examine data
dat <- dat.maire2019$dat
dat[-10]
#> site station site_station s1 vars1 s2 vars2 s3 vars3
#> 1 site1 sta1 site1_sta1 168 3502.7424 9 2301.0000 -109 2301.0000
#> 2 site1 sta2 site1_sta2 123 2301.0000 -9 2301.0000 -71 1603.4889
#> 3 site2 sta1 site2_sta1 302 5846.0000 -213 13738.9074 -1 5846.0000
#> 4 site2 sta2 site2_sta2 220 12815.9330 -306 8523.6120 162 10331.2344
#> 5 site2 sta3 site2_sta3 350 3154.7614 -220 15295.4021 56 5846.0000
#> 6 site2 sta4 site2_sta4 337 1890.6559 -336 11428.8040 180 7707.7479
#> 7 site2 sta5 site2_sta5 233 8644.3041 -389 10296.2071 231 2577.2668
#> 8 site2 sta6 site2_sta6 283 5846.0000 -460 9629.2758 148 5846.0000
#> 9 site2 sta7 site2_sta7 353 10344.5677 -320 12964.8288 300 5846.0000
#> 10 site3 sta1 site3_sta1 177 2562.0000 -140 2562.0000 -97 2562.0000
#> 11 site3 sta2 site3_sta2 229 4301.7270 -111 2562.0000 29 2562.0000
#> 12 site4 sta1 site4_sta1 248 4606.0582 -126 955.6867 117 3338.5788
#> 13 site4 sta2 site4_sta2 197 5436.9501 -34 2301.0000 -16 2301.0000
#> 14 site5 sta1 site5_sta1 93 950.0000 -14 1160.7161 21 950.0000
#> 15 site5 sta2 site5_sta2 34 468.8432 3 697.0000 -21 446.6578
#> 16 site5 sta3 site5_sta3 61 594.4956 -16 950.0000 47 950.0000
#> 17 site5 sta4 site5_sta4 61 950.0000 96 950.0000 44 950.0000
#> 18 site6 sta1 site6_sta1 271 4165.3333 -187 6756.4437 -167 4165.3333
#> 19 site6 sta2 site6_sta2 319 4165.3333 -182 2885.4519 -98 3567.5292
#> 20 site7 sta1 site7_sta1 14 817.0000 -41 817.0000 -115 817.0000
#> 21 site7 sta2 site7_sta2 61 1499.0587 -59 817.0000 -75 817.0000
#> 22 site8 sta1 site8_sta1 305 9035.2651 -123 2842.0000 -68 2842.0000
#> 23 site8 sta2 site8_sta2 315 5096.2897 58 2842.0000 41 2842.0000
#> 24 site8 sta3 site8_sta3 195 2842.0000 -31 2842.0000 117 2842.0000
#> 25 site9 sta1 site9_sta1 308 11395.6877 243 5497.1710 -3 1568.0952
#> 26 site9 sta2 site9_sta2 345 5395.0077 316 3461.6667 -139 3461.6667
#> 27 site9 sta3 site9_sta3 294 3461.6667 -89 3461.6667 -193 3461.6667
#> 28 site9 sta4 site9_sta4 318 5212.0340 -78 3461.6667 -123 8405.0704
#> 29 site10 sta1 site10_sta1 114 739.1046 -37 950.0000 0 950.0000
#> 30 site10 sta2 site10_sta2 92 2640.7189 -62 1096.6667 -46 1096.6667
#> 31 site11 sta1 site11_sta1 50 2021.0911 -24 1096.6667 79 1096.6667
#> 32 site11 sta2 site11_sta2 309 4550.3333 -112 4550.3333 -12 4550.3333
#> 33 site11 sta3 site11_sta3 225 3107.6097 -75 4550.3333 -6 4550.3333
#> 34 site11 sta4 site11_sta4 37 1096.6667 -44 1096.6667 11 1096.6667
#> 35 site11 sta5 site11_sta5 44 1661.3690 -5 950.0000 46 950.0000
### copy distance matrix into 'dmat' and examine first 5 rows/columns
dmat <- dat.maire2019$dmat
dmat[1:5,1:5]
#> site1_sta1 site1_sta2 site2_sta1 site2_sta2 site2_sta3
#> site1_sta1 0 6 10000 10000 10000
#> site1_sta2 6 0 10000 10000 10000
#> site2_sta1 10000 10000 0 1 1
#> site2_sta2 10000 10000 1 0 1
#> site2_sta3 10000 10000 1 1 0
### load metafor package
library(metafor)
### fit a standard random-effects model ignoring spatial correlation
res1 <- rma.mv(s1, vars1, random = ~ 1 | site_station, data=dat)
res1
#>
#> Multivariate Meta-Analysis Model (k = 35; method: REML)
#>
#> Variance Components:
#>
#> estim sqrt nlvls fixed factor
#> sigma^2 10522.1760 102.5777 35 no site_station
#>
#> Test for Heterogeneity:
#> Q(df = 34) = 191.4837, p-val < .0001
#>
#> Model Results:
#>
#> estimate se zval pval ci.lb ci.ub
#> 187.5809 20.0424 9.3592 <.0001 148.2984 226.8633 ***
#>
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
### fit model allowing for spatial correlation
res2 <- rma.mv(s1, vars1, random = ~ site_station | const, struct="SPGAU",
data=dat, dist=list(dmat), control=list(rho.init=10))
res2
#>
#> Multivariate Meta-Analysis Model (k = 35; method: REML)
#>
#> Variance Components:
#>
#> outer factor: const (nlvls = 1)
#> inner term: ~site_station (nlvls = 35)
#>
#> estim sqrt fixed
#> tau^2 8945.8842 94.5827 no
#> rho 15.0568 no
#>
#> Test for Heterogeneity:
#> Q(df = 34) = 191.4837, p-val < .0001
#>
#> Model Results:
#>
#> estimate se zval pval ci.lb ci.ub
#> 176.5775 26.3986 6.6889 <.0001 124.8372 228.3178 ***
#>
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
### add random effects for sites and stations within sites
res3 <- rma.mv(s1, vars1, random = list(~ 1 | site/station, ~ site_station | const), struct="SPGAU",
data=dat, dist=list(dmat), control=list(rho.init=10))
res3
#>
#> Multivariate Meta-Analysis Model (k = 35; method: REML)
#>
#> Variance Components:
#>
#> estim sqrt nlvls fixed factor
#> sigma^2.1 7158.3492 84.6070 11 no site
#> sigma^2.2 0.0000 0.0039 35 no site/station
#>
#> outer factor: const (nlvls = 1)
#> inner term: ~site_station (nlvls = 35)
#>
#> estim sqrt fixed
#> tau^2 3425.5862 58.5285 no
#> rho 12.8755 no
#>
#> Test for Heterogeneity:
#> Q(df = 34) = 191.4837, p-val < .0001
#>
#> Model Results:
#>
#> estimate se zval pval ci.lb ci.ub
#> 182.1199 31.2808 5.8221 <.0001 120.8107 243.4291 ***
#>
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
### likelihood ratio tests comparing the models
anova(res1, res2)
#>
#> df AIC BIC AICc logLik LRT pval QE
#> Full 3 402.3380 406.9171 403.1380 -198.1690 191.4837
#> Reduced 2 423.8050 426.8577 424.1921 -209.9025 23.4670 <.0001 191.4837
#>
anova(res2, res3)
#>
#> df AIC BIC AICc logLik LRT pval QE
#> Full 5 403.7355 411.3673 405.8783 -196.8677 191.4837
#> Reduced 3 402.3380 406.9171 403.1380 -198.1690 2.6025 0.2722 191.4837
#>
### profile likelihood plots for model res2
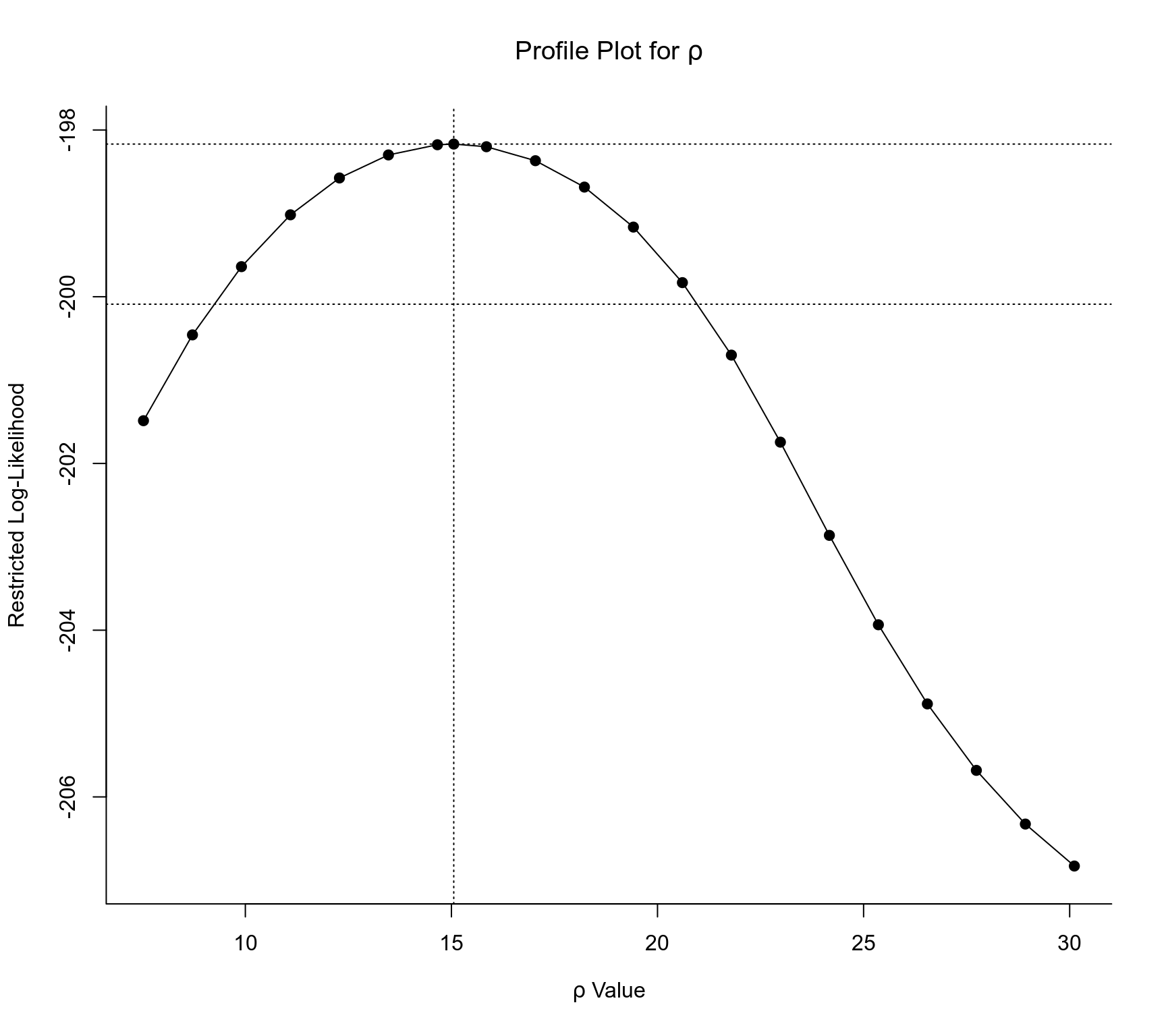
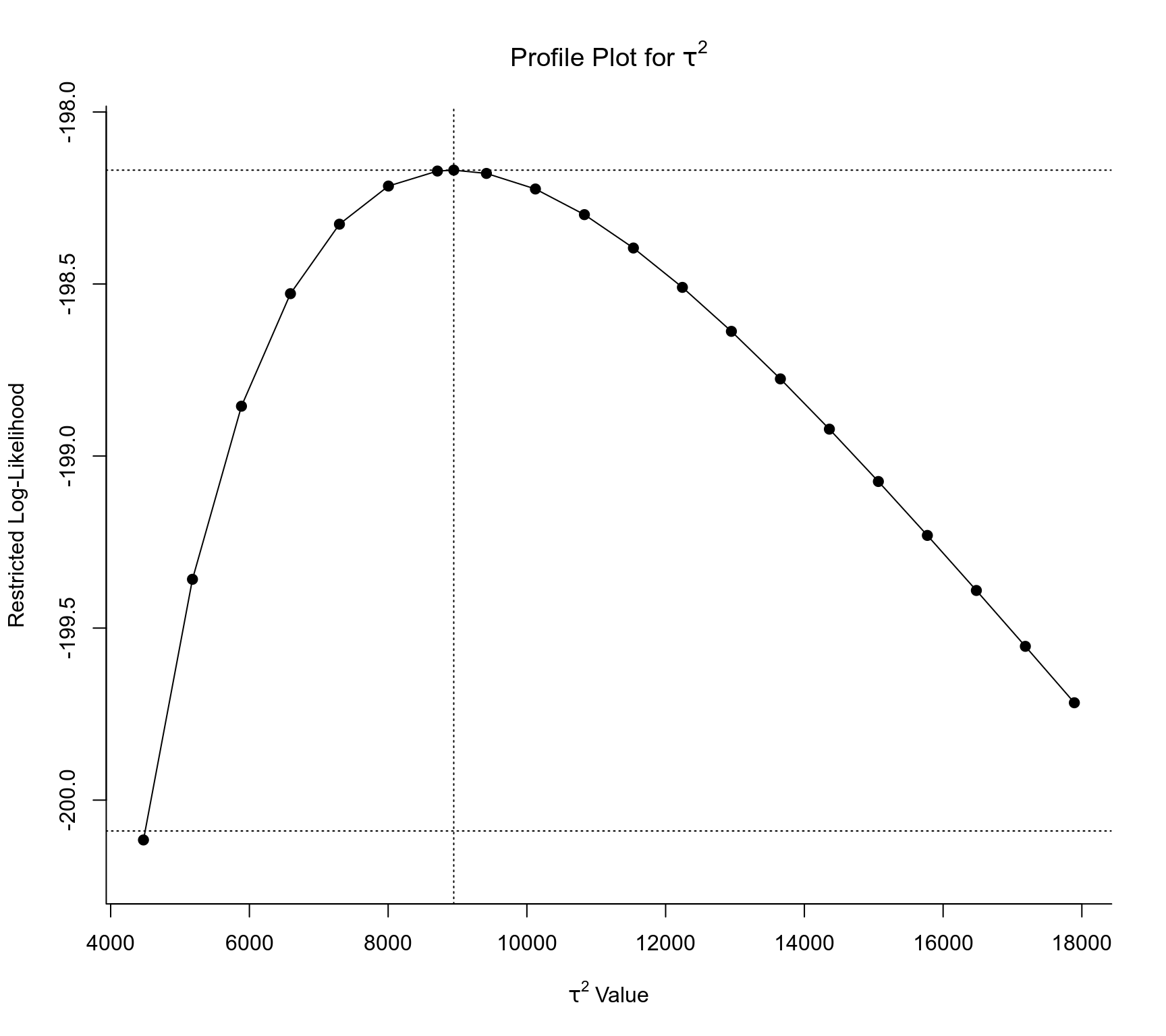
profile(res2, cline=TRUE)
#> Profiling tau2 = 1
#> Profiling rho = 1
 ### effective range (river-km for which the spatial correlation is >= 0.05)
sqrt(3) * res2$rho
#> [1] 26.07908
### note: it was necessary to adjust the starting value for rho in models
### res2 and res3 so that the optimizer does not get stuck in a local maximum
profile(res2, rho=1, xlim=c(0,200), steps=100)
### effective range (river-km for which the spatial correlation is >= 0.05)
sqrt(3) * res2$rho
#> [1] 26.07908
### note: it was necessary to adjust the starting value for rho in models
### res2 and res3 so that the optimizer does not get stuck in a local maximum
profile(res2, rho=1, xlim=c(0,200), steps=100)